Never Worry About Tax Filing Again : 3 Business Dates to Remember for Efficient Tax Planning
If you are running any Hong Kong limited company, you should not miss the following deadline of statutory filing. Take out your favorite calendars apps, like the Google Calendar that my colleagues are using happily, and block these dates so you and your teammates will always get prepared ahead.
Before we start, I need to remind you that these filing obligations below are spontaneously bound to every Hong Kong limited company and thus its shareholders, directors, and managers. Therefore, the authorities do not accept excuses like “I did not receive the notice.” or “I’m not in Hong Kong.” on non-compliance which will lead to penalties, punishments, or prosecutions.
Secondly, if any filing demands come with government bills, you must settle them on the submission of the return. Fortunately, the departments of the Hong Kong government adopt various electronic payment methods; you will find the government-supported payment method here.
1. Anniversary Date of Incorporation
It is the “birthday” of your company, in short. On this date, the Companies Registry and the Inland Revenue Department, the company registration authority and tax authority of Hong Kong, demand the Annual Return, which is for the renewal of the Certificate of Incorporation, and Business Registration Renewal respectively.
Annual Return
The annual return is a specific form codenamed as NAR1, requires your company to file its necessary details, e.g. company name, registered office address, members’ particulars, and share capital. Primarily, the form has the same requirement as your company incorporation form NNC1.
The deadline for submission is on the 42nd calendar day after the anniversary date.
Standard government fee is HK$105.
The late penalty is on the financial bid, the later the submission, the more the penalty is imposed.
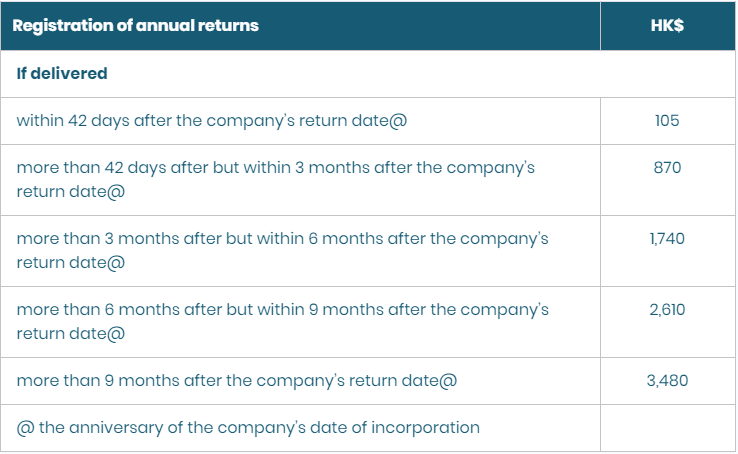
Source: https://www.cr.gov.hk/en/services/fees.htm
Failure to comply with the provision of the Companies Ordinance will result in prosecution in the Magistrates’ Courts: the maximum fine is HK$50,000 plus daily default fine of HK$1,000.
Pay attention: If you have made any change to those company’s particulars, e.g. change of company name, you cannot file the new information of the annual return unless you have notified the CR by submitting specific forms immediately after the changes. In other words, the annual return should reflect the record in the Company Registrar of your company, but not to report of changes.
Business Registration Renewal
Business Registration Certificate is the license of carrying on businesses and the registration of taxpayers as a business entity in Hong Kong. The fee is the same as that of the application of a new license.
Around two weeks before the expiry date of your current certificate, the IRD will post the demand note which is printed in A4 size paper and bundled with the new license posted to your company’s business address. Then, you have to settle the government fee and levy to complete the renewal procedure; then the attached certificate will come into effect.
Failure to comply with the provisions of the Business Registration Ordinance is liable to a maximum penalty of a fine of $5,000 and imprisonment for one year.
Points to note: This paper does not entitle your company to do ANY business in Hong Kong because you need to apply for specific licenses before your company engages in restricted business activities, like banking and medical services. The usage of the certificate is for taxation purposes here. You can elect to either a 1-year or 3-year license of the business registration, although you will not entitle to any discount in the 3-year option.
2. Hong Kong Government Fiscal Year End Date
Every fiscal year of the Hong Kong government begins on 1 April and ends on 31 March of the following year. The IRD follows the same schedule to mark the tax assessment year of Hong Kong, also known as the “tax year”. For example, the tax year 2022/23 refers to the period from 1 April 2022 to 31 March 2023.
These dates are especially relevant to employers and employees. For employers, they have to prepare the payroll records within the tax year for their employees and file on the Employer’s Return. For employees, including the directors of the company, their personal income sourced from employment within the tax year are subject to Salaries Tax.
The IRD sends out the Annual Employer’s Return demand note to the Hong Kong businesses on the first working day of April to request the payroll information of the previous tax year. The standard submission deadline of the Employer’s Return is one month after its issue date.
IRD also sends out the Individual Tax Return and Corporate Tax Return on the first working day of May. Again, the regular submission deadline is one month after their issue date, respectively.
We will take an in-depth look at the Corporate Tax Return because it affects limited companies.
Be reminded that delays in submitting your tax return will lead to higher penalties and could lead to prosecution.
3. Accounting Date
In the terminology of Hong Kong taxation, the Accounting Date is end date of the financial year for a corporation, i.e. a corporate taxpayer in Hong Kong.
Under the principle of simple taxation, you can declare any calendar day (or even lunar calendar day!) as the Accounting Date for your Hong Kong company on your annual Profits Tax returns.
The Accounting Date defines a timeframe for reporting your tax and accounting matters. For example, a company’s accounting date is 31 May, the period of reporting is from 1 June 2021 to 31 May 2022 in the tax year 2022/23. It’s because the IRD can legally demand the tax from your profits which you have earned, when you receive the tax return in May 2023, you only have the accounting and tax matters reflecting your latest and completed accounting period.
For foreign enterprises, the flexibility setting accounting date can help them to align their Hong Kong taxation and accounting matters with that in their home country; For others, this flexibility could be a no-cost option to gain 12 months ahead of the deadline, we have a post on our blog for the details.
Once you have marked the Accounting Date, you need to schedule the following tax and accounting obligation orderly:
- Accounting (Business Accounting Service)
- Statutory Audit (Auditor’s Service)
- Profits Tax Return Filing (Tax Representative Service)
Remarks: if you want to seek help to handle these responsibilities from external parties, you can refer to the keywords in ().
Accounting & Statutory Audit
The products of the accounting and statutory audit is a set of audited accounting books and auditor’s reports, which are commonly and collectively known as “audit reports”. Since you are only required to file your Profits Tax Return with the audit report attached annually, you can begin these tasks after the Accounting Date.
Tax Return Filing
Filing the tax return is the final step. You should make a tax calculation before you input the details on the form.
AsiaBC offers full-fledged company maintenance, accounting and taxation services, you have ensured a hassle-free experience with our support.

![Asia Business Centre (Asia Business Centre (AsiaBC) [HK+SG Bank Account Opening / Company Formation / Company Secretary / Accounting & Tax])](https://asiabc.com.hk/wp-content/uploads/Blog-Banner-Never-Worry-About-Tax-Filing-Again-3-Business-Dates-to-Remember-for-Efficient-Tax-Planning-1030x464.png)

![Asia Business Centre (Asia Business Centre (AsiaBC) [HK+SG Bank Account Opening / Company Formation / Company Secretary / Accounting & Tax])](https://asiabc.com.hk/wp-content/uploads/Blog-Banner-3-Best-Ways-HK-Startups-Claim-Tax-Deductions-80x80.png)
![Asia Business Centre (Asia Business Centre (AsiaBC) [HK+SG Bank Account Opening / Company Formation / Company Secretary / Accounting & Tax])](https://asiabc.com.hk/wp-content/uploads/Blog-Banner-Entrepreneurs-Guide-to-Corporate-Accounting-Statutory-Audit-80x80.png)



